| The Keyboard Window

The Keyboard window enables the entry of musical information via the
use of its virtual keyboard or by typing directly on the computer
keyboard. It also allows pitch bend and modulation (MIDI controller
number 1) to be entered. Modulation can alternatively be entered via
the mouse wheel.
Note:
There
is a limit on most computer keyboards as to the number of detectable
keys at one time so you may be limited to certain combinations of keys
when trying to play chords.
The keys on the
computer keyboard are arranged for a more than 2 octave range. The
lower octave, corresponding to a standard piano keyboard, contains the
keys:
Q,2,W,3,E,R,5,T,6,Y,7,U,I
Note: the white keys occur all in a row.
The upper octave contains the keys:
Z,S,X,D,C,V,G,B,H,N,J,M, and the comma key. Some
extra notes occur past the end of the higher octave.
The '[' and ']' keys on the computer keyboard are
used to change the current octave.
Real-Time Arpeggiator
The
keyboard window also houses the Real-Time Arpeggiator. The Real-Time
Arpeggiator features multiple arpeggiation patterns; multiple
arpeggiation methods; octaves control; sync control; swing control;
steps control; pattern UI area with 16 X 3 steps, each with quick
independent control over transpose, velocity and duration via popup;
latching; retriggering; initialize pattern; randomize pattern; shuffle
pattern; load and save presets; copy and paste; transpose up and down;
remote control of arp parameters; spread slider for guitar like
strumming; left and right arrow keys can be used to rotate the current
pattern; and more.
The Real-Time Arpeggiator works with
all soft synth plugs and external MIDI and is now available for Metro
SE and Metro LX users.
Windows Version
of the Keyboard window with arpeggiator active.

Click in the picture below for an
explanation of particular functions.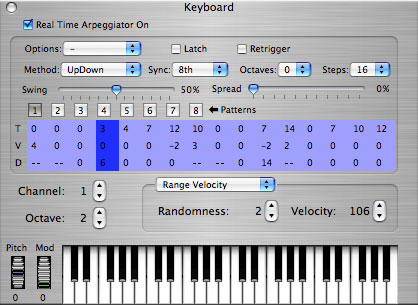
Click
the 'real time arpeggiator on' switch to toggle the arppeggiator on and
off.
Options:
The
options menu provides functionality for controlling the powerful
arpeggiator functions. Use 'Open Preset...' to load a preset from the
file system. Presets include all parameters and patterns. Use 'Save
Preset As..' to save a copy of the current arpeggiator settings.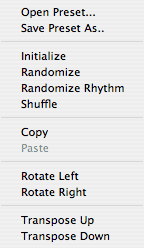
'Initialize' sets all arpeggiator settings to
their defaults.
'Randomize'
is a powerful function that creates a random pattern. It makes
intelligient decisions to try to produce more useful results.
'Randomize Rhythm' is the same as Randomize
accept that it does not affect pitch information.
'Shuffle' rearranges the current pattern by
shuffling the steps.
'Copy' copies the current pattern for use by the
paste command.
'Paste'
pastes the current contents of the arpeggiator clipboard over the
current pattern. This function is only available if an arpeggiation
pattern had previously been copied and it is not undoable.
'Rotate Left' and 'Rotate Right' rotates the
current pattern in the direction specified.
'Transpose Up' and 'Transpose Down' transposes the
current pattern up or down one half step respectively.
Latch:
Latch allows the arpeggiator to continue after the
keys come up.
Retrigger:
Normally
keys pressed in the middle of pattern are synced based on the position
in the pattern and start in the middle. If Retrigger is checked, the
pattern will restart from the beginning regardless of the current
sequencer time.
Method:
The method popup determines how the arpeggiation
is processed.
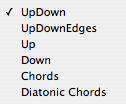 UpDown:
Notes are sorted and processed from lowest to highest pitch and then
highest to lowest. The highest and lowest notes are only processed
once. UpDown:
Notes are sorted and processed from lowest to highest pitch and then
highest to lowest. The highest and lowest notes are only processed
once.
UpDownEdges: Same as UpDown but the highest and
lowest notes are processed twice.
Up: Notes are processed from lowest to highest.
Down: Notes are processed from highes to lowest.
Chords: Notes are played at each step as they are
entered.
Diatonic
chords: Same as Chords except that transposed notes are tranposed in
the current scale based on the time signature of the section.
Sync:
This setting determines the duration of each step
in the currently selected pattern.
Octaves:
The
Octaves setting within the arpeggiator section determines the number of
extra octaves added to the arpeggiator function. Octaves are always
added higher in pitch.
The Octaves setting outside of the
arpeggiator section determines what the first note of the onscreen
keyboard will be. You may also use the '[' and ']' keys on the computer
keyboard to change the current octaves setting.
Steps:
This setting determines the number of steps in the
currently selected pattern.
Swing:
This
setting determines the swing of the current pattern. Swing of 50% is no
swing. Otherwise swing affects the position of every other note in the
pattern.
Spread:
This setting causes notes in the pattern to be
spread out or flammed by the percent specified.
Patterns:
Click on the number box to select the current
arpeggiator pattern. The current pattern is highlighted.
Arpeggiatior Pattern:
Transpose
Row:
Each
item in the row represent the number of half steps the currently held
notes will be transposed and played for the current arpeggiation step.
Velocity
Row:
Each
item in this row represent the amount of velocity change that will be
applied to currently held notes for the current arpeggiation step.
Duration
Row:
Each
item in this row represent the amount of duration change that will be
applied to currently held notes for the current arpeggiation step. '--'
means that the current step ties its duration to the following step.
'R' means that no notes are played during this step and a rest occurs
instead.
Chord Row:
Each item in this row represent the index of the
note to play at the current arpeggiator step. '--'
is the normal setting. In the normal setting the note(s) will play
based on the current arpeggiator method (see above). Here is an
explanation
of the possible values to be played in this row:
| Indicator |
Explanation |
| 'C' or Chord |
Play all the notes currently being held
down. |
| 'L' or '1' or lowest |
Plays the lowest pitch note. |
| 'H' or highest |
Plays the highest pitch note. |
| '--' |
Play the current position determined by the
arpeggiator method. |
| 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 or 7 |
Play the numerically indexed note based on
the sorted order of notes
currently held down. |
Channel:
This setting determines which MIDI channel is sent
for MIDI messages originating from the keyboard window.
Velocity:
If
range velocity is selected the velocity is the current velocity with
the randomness setting applied. If mouse velocity is selected the
velocity will be based on the current horizontal position of the mouse
in the velocity region of the keyboard window.
Keyboard:
Click on the keyboard to play (or record) notes at
the designated pitch and with the velocity specified.
See Also:
|